Git & GitHub:
what is Git?

Git is a version control system that helps you keep track of changes made to your code over time.
It allows you to collaborate with others on a project, keep track of different versions of your code, and easily revert to previous versions if needed.
what is GitHub?
GitHub is a website that allows you to store your code online and collaborate with others. It uses Git as its version control system, so you can keep track of changes made to your code over time, work with others on the same codebase, and easily share your code with the world.
Why it is important?
Tracking the changes and updates. We can see who made which changes. Git also provides when and why a change was made.
Allowing them to work collaboratively. Software development projects usually require many people to work together. Git provides developers with a systematic way of doing that. Thus, the developers focus on the project instead of extensive communication sessions between the other developers.
Version Control:
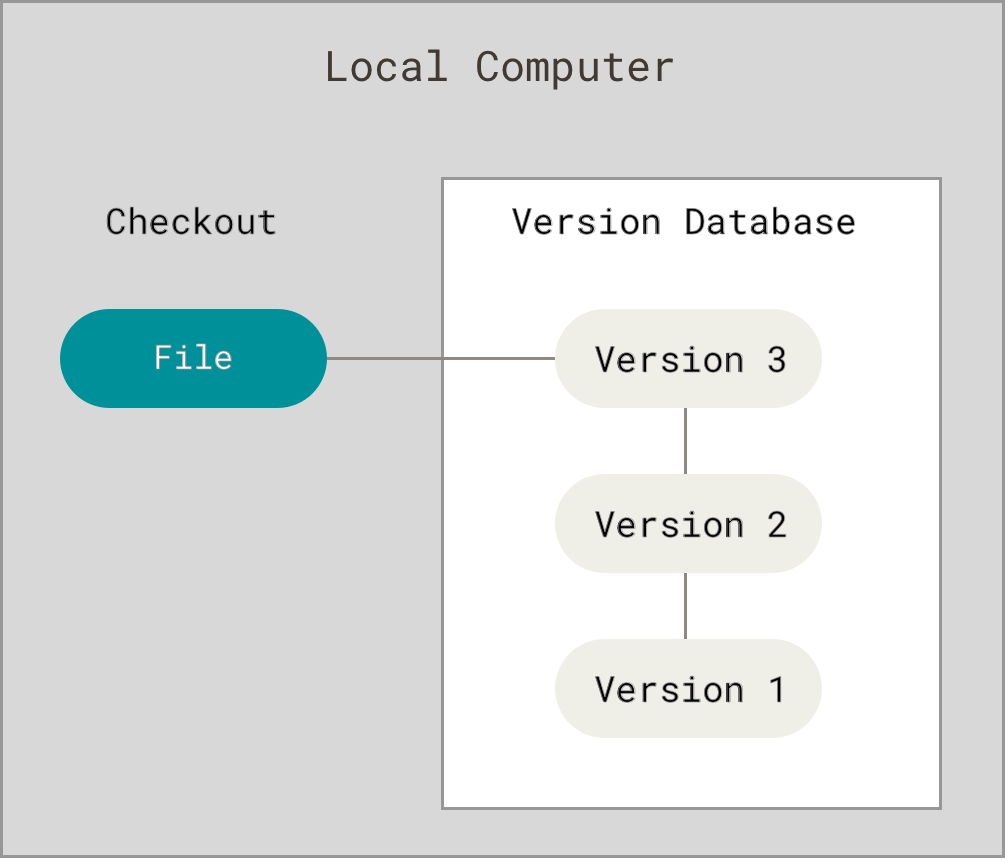
In the git version control system if you put anything it will have a version it will have the time it will have an author it will have a hash_id.
Hash - when you delete a file in git and one day you need that file that you have deleted so, in that case, u retrieved the file hash is a number and that number is stored in git that's why you retrieved the file.
Types Of Version Control Systems?
versions controls systems are two types:
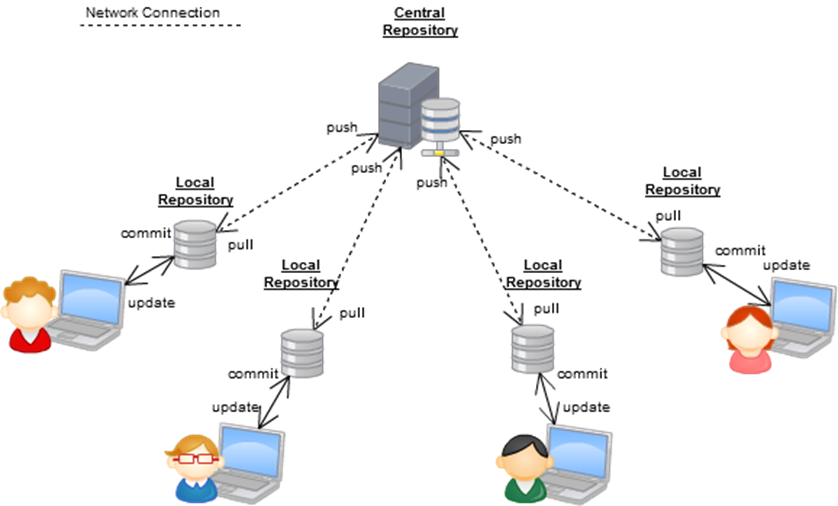
Distributed version control system(DVCS)
Git is a Distributed Version Control System.
In DVCS every contributor has a local copy or clone of the main repository i.e everyone maintenance a local repo of their own which containers all the files & metadata present in the main repository.
Centralized version control system(CVCS)
GitHub is a Centralized Version Control System
suppose u have a repository and everybody came and distribute the code and suddenly the server is crash, in that case, everything in your code is gone.
Advantages of Git:
Git has several advantages, including:
1. Version Control: Git allows you to keep track of changes made to your code over time, making it easy to revert to previous versions if needed.
2. Collaboration: Git makes it easy to collaborate with others on a project, allowing multiple developers to work on the same codebase simultaneously.
3. Branching: Git allows you to create branches, which are separate versions of your code that can be worked on independently. This makes it easy to experiment with new features without affecting the main codebase.
4. Security: Git provides a secure way to store your code online, with multiple layers of encryption and authentication to protect your data.
5. Flexibility: Git can be used with a wide range of programming languages and development environments, making it a versatile tool for developers of all kinds.
Overall, Git is a powerful tool that can help developers work more efficiently, collaborate more effectively, and keep their code safe and secure.
Video Link Here 👇👇👇
Git Three Stages
Let us see the basic workflow of Git.
Step 1 − You modify a file from the working directory.
Step 2 − You add these files to the staging area.
Step 3 − You perform commit operation that moves the files from the staging area. After push operation, it stores the changes permanently to the Git repository.
Git Command
- Repository meaning is a simple folder
so firstly you install git
You can check the current version of git with git --version command.
git --version
git init
git version 2.34.1
The Git config the command is super helpful. Especially when you are using Git for the first time, or you have a new Git installation. This command will set up your identity - Name and Email address. And this information will be used with every commit.
git config --global user.name "Dev_Safia"
git config --global user.email "safiakhatoonami@gmail.com"
git config list the command will show all Git config properties
git config --list
user.name=Dev Safia
user.email=safiakhatoonami@gmail.com
mkdir git_tut_devops_batch
cd git_tut_devops_batch/
mkdir project{1..3}
project1 project2 project3
cd project1/
This is probably the first command you use to start a new project in Git. This command will create a blank new repository, and then you can store your source code inside this repo.
git init
ls -a
. .. .git
vim safia.txt
one thing is very important your repo is not blank otherwise it is not added and committed.
Git status is one of the important git commands.
Mainly git status shows
Your current branch.
List of files that are committed or pending changes.
git status
git add the command will be used to add new files to the staging area.
git add safia.txt (it will add a single file to your staging area)
git add * ( this option will add all the modified and new files to the staging area)
the git commit will add your changes to your local repository.
git commit -m "commit this file"
delete this file
rm -rf safia.txt
git status
and again restore the file in this case one thing is proven when you delete something then you retrieved again this thing with the help of the git restore command
Note: one question in my mind I delete without staging the file and then can retrieve the file so the answer is no u can't
git restore safia.txt
git log the command helps you to see all previous commit messages.
git log
git log --all
View only one line changes. It helps to have a quick look at previous commits.
git log --one line
You can view all differences of changes of each commit with -p option
git log -p
step 1: And now you create a repo in GitHub
Safia blog
step 2: and then create your local same as
mkdir safia_blog
step 3: and again go to your GitHub and copy the HTTPS code
git clone https://github.com/Safiakhatoon767/safia_blog.git
ls
safia_blog
cd safia_blog/
Video Link Here 👇👇👇
git init vs. git clone
A quick note: git init and git clone can be easily confused. At a high level, they can both be used to "initialize a new git repository." However, git clone is dependent on git init. git clone is used to create a copy of an existing repository. Internally, git clone first calls git init to create a new repository. It then copies the data from the existing repository.
How to push our local files and folders in GitHub
create a new repo in GitHub and local
mkdir DevOps
cd DevOps
git init
create some files in your local repo
touch safia{1..3}.txt
ls
safia1.txt safia2.txt safia3.txt
git add. (all files will add )
git commit -m "add this files"
show remote origin URL
git remote -v
Git remote command acts like a border, and If you need to connect with the outside world, you have to use the Git remote command. This command will connect your local repository to the remote.
git remote add origin https://github.com/Safiakhatoon767/safia-blog-1.git
git remote -v
origin github.com/Safiakhatoon767/safia-blog-1.git (fetch)
origin github.com/Safiakhatoon767/safia-blog-1.git (push)
In simple words, the git push command is used to send your local changes to the remote repo.
git push origin master
so in my case, I find the error such that remote: Support for password authentication was removed on August 13, 2021. remote: Please see docs.github.com/en/get-started/getting-star.. for information on currently recommended modes of authentication. fatal: Authentication failed for 'github.com/Safiakhatoon767/Devops.git' maybe you didn't find an error
How to solve this error:
step 1: go to GitHub settings
step 2: go to the developer setting
step 3: personal access token
step 4: Tokens classic
step:5 generate a new token
step 6: generate a new token classic
step 7: copy your access token now.
step 8: go to your local terminal and paste a URL like this
git remote set-url origin https://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@github.com/Safiakhatoon767/DevOps.git
git push origin master
What is a git repository?
A Git repository is a place where developers store and manage their code files for a software project, allowing them to collaborate, track changes, and work together on the same codebase.
How Git is different from Github?

Difference between git and GitHub :
Git :
Git is based on CLI (Command line interface)
Git installed locally
Open Source Licence.
GitHub :
GitHub is based on GUI (Graphical user interface)
GitHub hosted in a web
Include a free tier and a pay-for-use tier.
What does git clone do?
It is used to point to an existing repository and make a clone or copy of that repository in a new directory, at another location.
What is a conflict and how will you resolve it?
A conflict in Git occurs when two or more people make changes to the same part of a file or project, resulting in a merge conflict. To resolve it, you need to review the conflicting changes, decide which changes to keep, and manually edit the file to combine the changes. Once the conflict is resolved, you can commit the changes to the repository.
What is the difference between git pull and git fetch?
In easy and short explanation, git fetch downloads the changes from the remote repository to your local repository, but does not merge them with your current branch. Whereas, git pull downloads the changes from the remote repository and automatically merges them with your current branch.

Git pull = git fetch + git merge
How will you create a git repository?
To create a Git repository, you can navigate to the directory where you want to store your project, and then use the command git init. This will initialize an empty Git repository in the current directory.
Tell me something about git stash.
git stash is a command in Git that allows you to temporarily save changes that are not yet ready to be committed. It stores the changes in a "stash" and reverts your working directory to the last commit, allowing you to work on a different branch or fix a bug before returning to the original changes.

Why do we not call git “pull request” as “push request”?
We do not call Git "pull request" as "push request" because a pull request is a request to merge changes from one branch to another, while a push request would imply a request to push changes from one branch to another. In Git, pushing changes means sending them to a remote repository, while pulling changes means getting them from a remote repository. Therefore, a pull request is a more accurate term for requesting changes to be merged into a branch.

what is a fork?
A fork is a copy of a repository.
How do I completely disconnect a local Git repository from all remote branches?
git remote rm origin
Difference between git clone and git init?
git clone the command will use an existing repository to copy. There is one main difference between the git init and git clone.
You will use the Git clone when you need to make a copy on an existing repository. The git clone command internally uses the git init command first and then checks out all its contents.
Difference between a GitHub fork and a Git clone?
FORK:

1. Forking is done on the GitHub Account.
2. Forking a repository creates a copy of the original repository on our GitHub account.
3. Forking is a concept
4. Forking is just containing a separate copy of the repository and there is no command involved
CLONE:
Cloning is done using Git
Cloning a repository creates a copy of the original repository on our local machine.
Cloning is a process.
Cloning is done through the command git clone and it is a process of receiving all the code files to the local machine.
What is the difference Between Main Branch and Master Branch??
when a repo is initialized in Git a branch will be created by default. This default branch is called MASTER while Github has a default branch when we create any repository which is called MAIN.
Video Link Here 👇👇👇
ADVANCED GIT COMMAND:
BRANCH
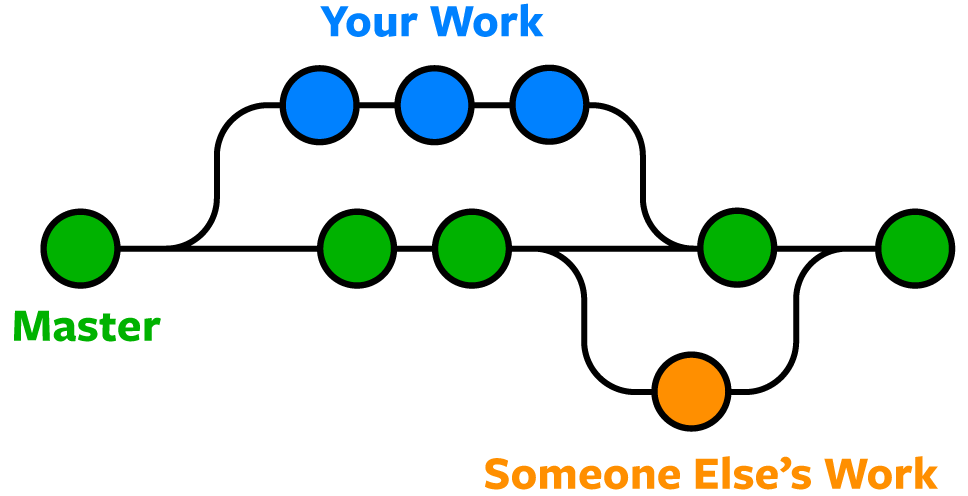
Most of the time, you have multiple branches in your Git repository. In simple terms, the branch is an independent line of code development.
product is the same so one repository but a different task.
Each task has one separate branch.
changes are present in that particular branch.
The default branch is "Master"
NOTE: The file Created in the workspace will be visible in any of the branch workspaces until you commit once you commit then that file belongs to that particular branch.
you can create any number of branches.
branch concepts useful for parallel development
when creating new branch data from the existing branch is copied to a new branch.
command:
all commit is shown
git log --one lineshow branch
git branchcreate a new branch
git branch <branch name>orgit checkout -b<branch_name>To switch branch
git checkout <branch name>delete branch
git branch --delete <branch name>delete branch
git delete -D <branch name>(forcefully delete)
git status (it is showing currently what is your branch)
if you want to switch and create a new branch, you can use the checkout command with the -b option.
git checkout -b feat/add_Devops (create a new branch)
touch Devops.txt
git add Devops.txt
git commit -m "add this file"
git status
git push origin feat/add_Devops (New branch is created on GitHub)
here feat is for feature it is my branch name you can choose according to you
switch to the master branch
git checkout master
Question: What is a Git branch, and how do you create and switch between branches?
Answer: A Git branch is a separate line of development that allows you to work on new features or fixes without affecting the main codebase. Creating a branch allows you to experiment with changes without worrying about breaking anything in the main branch.
To create a new branch in Git, you can use the git branch command followed by the name of the new branch. For example, to create a new branch called "feature-branch", you would use the following command:
git branch feature-branch
To switch to the new branch, you can use the git checkout command followed by the name of the branch. For example, to switch to the "feature-branch", you would use the following command:
git checkout feature-branch
Alternatively, you can create and switch to a new branch in one step by using the git checkout command with the -b flag. For example, to create and switch to a new branch called "feature-branch" in one step, you would use the following command:
git checkout -b feature-branch
Once you're working in a branch, you can make changes and commit them as usual. When you're ready to merge your changes back into the main branch, you can use the git merge command to combine the changes.
Video Link Here 👇👇👇
MERGE:(copy-paste)
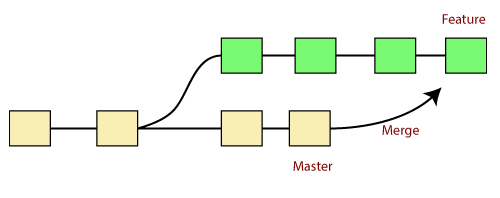
Git merge helps you to integrate changes from two branches into a single branch.
we use a pulling mechanism to merge branches
when you pull your code in the master branch it also exists code in that branch.
you can't merge branches of the different repositories e.g like your friend repo
for merge.
git merge <branch name>
to verify the merge
git log
to push central repo like GitHub
git push origin master
Tasks For You :
What is
git mergeand what does it do?What is the difference between
git mergeandgit rebase?What is a merge conflict and how do you resolve it?
Can you use
git mergeto merge two branches that have diverged significantly?What is a fast-forward merge and when does it occur?
How do you use
git mergeto merge a feature branch into the main branch?What is a three-way merge and how does it work?
Can you use
git mergeto merge a branch into multiple other branches at once? If so, how?How do you use
git mergeto undo a merge that has already been completed?What are some best practices for using
git mergein a team environment?
I hope this helps!
Video Link Here 👇👇👇
Git conflict

suppose you have two branches and you create a file of the same name in both branches but whenever you merge these branches in that time
the important thing is data are different in both files in that case conflict occurs.
conflicts occur when you merge branches.
Q: What is a merge conflict in Git and how do you resolve it?
Ans: A merge conflict occurs when Git is unable to automatically merge changes from two different branches. This can happen when two or more people are working on the same file at the same time and make different changes to it. When you try to merge these changes, Git will notify you of the conflict and ask you to resolve it manually.
To resolve a merge conflict, you need to open the file(s) that have conflicts and manually edit them to include the changes you want to keep. You can use a diff tool to compare the conflicting versions of the file and decide which changes to keep. Once you've resolved the conflict, you need to stage the changes and commit them to complete the merge.
Tasks For You :
Can you describe a time when you had to resolve a conflict with a coworker or team member? How did you handle the situation, and what was the outcome?
What is your approach to managing conflicts in the workplace? Can you give an example of a successful outcome from a conflict you managed?
How do you handle conflicts with someone who has a different communication style or personality than you?
Can you give an example of a time when you had to navigate a conflict with a superior or someone in a position of authority? How did you approach the situation?
In your opinion, what is the most effective way to resolve conflicts in a team setting?
How do you ensure that all parties involved in a conflict feel heard and understood during the resolution process?
Can you describe a time when you had to negotiate a compromise between two conflicting parties? What was your approach, and how did you resolve it?
How do you handle conflicts that arise due to cultural or generational differences in the workplace?
Can you give an example of a time when you had to apologize for your actions during a conflict resolution process? How did you take responsibility for your behaviour and work towards a solution?
What steps do you take to prevent conflicts from arising in the workplace in the first place?
Video Link Here 👇👇👇
Git Stashing
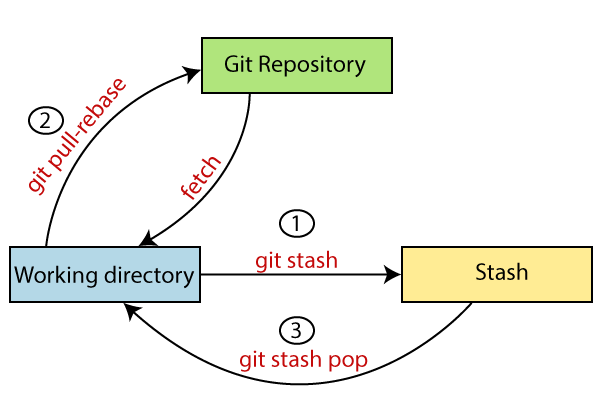
what is Git Stash?
Git stash is a command in Git that allows you to temporarily save changes that are not yet ready to be committed or pushed to a remote repository. It takes your current working directory and saves it on a stack of unfinished changes that you can return to later. This can be helpful when you need to switch to a different branch or work on a different task without committing incomplete changes. Once you're ready to continue working on the incomplete changes, you can use the git stash and apply the command to restore them to your working directory.
This Git command temporarily stores your modified files. You can work in stashed with the following Git command.
A stash is a temporary storage.
To stash, an item only applies to modified files, not new files.
To stash an item
git stash
To see stashed items list
git stash list
To apply stashed items
git stash apply stash {0}
{0} --------- current files
{1}----------last files
Then you can add and commit to clear the stash item
git stash clear
TASKS FOR YOU :
What is Git stash and why is it used?
Can you explain the difference between git stash apply and git stash pop?
How can you view the list of stashes that you have saved?
Can you stash changes selectively instead of stashing everything at once?
How can you clear all stashes from the stack?
What happens if you stash changes that conflict with changes in the current working directory?
Can you use git stash to save changes in a remote repository?
How can you create a new branch from a stash?
Can you stash untracked files as well?
What is the command to apply a stash to a different branch?
Video Link Here 👇👇👇
Git Restore:
Git restore is a command in Git that allows you to undo changes made to a file or directory and restore it to a previous state.
The "restore" command helps to unstaged or even discard uncommitted local changes.
git restore <file name>
Advantages of Git Restore :
The advantage of using Git restore is that it allows you to undo changes made to a file or directory and restore it to a previous state.
This can be helpful if you accidentally delete or modify a file and want to revert to a previous version.
Git restore also allows you to selectively restore parts of a file or directory, which can save time and make it easier to manage changes in a Git repository.
Tasks For You :
What does the
git restorecommand do?What is the difference between
git restoreandgit reset?How do you use
git restoreto discard changes in a specific file?Can you use
git restoreto restore a deleted file? If so, how?What is the difference between
git restore --sourceandgit restore --staged?How do you use
git restoreto unstaged changes?How do you use
git restoreto restore a file to a specific commit?What is the syntax for using
git restoreto restore a file to a specific commit?How do you use
git restoreto restore a file to its state in the previous commit?Can you use
git restoreto restore a file that has been modified but not yet committed? If so, how?
I hope this helps!
Video Link Here 👇👇👇
Git Reset
Git reset is a command that allows you to move the current branch pointer to a different commit. This can be useful if you need to undo changes that have been made to your code. There are three modes of git reset: soft, mixed, and hard.
Soft reset moves the branch pointer to a different commit, but leaves the changes you made in the working directory.
Mixed reset moves the branch pointer and resets the staging area to match the commit you specify. This means that changes you made are not lost, but they are no longer staged for commit.
Hard reset moves the branch pointer and resets the staging area to match the commit you specify. This also means that any changes you made are completely removed and cannot be recovered.
It is important to note that git reset should be used with caution as it can potentially delete changes that have not been committed yet.
The git reset command is used to remove a file from the staging area.
To reset the staging area
git reset <filename>
git reset.
To reset the changes from both the staging area and working directory at a time
git reset --hard (conflicts)
git reset --soft (smooth)
git reset --mixed (default)
Tasks For You :
What is the difference between git reset and git revert?
How do you undo the changes made in the last commit using git reset?
What is the difference between soft, mixed, and hard resets in Git?
Can you reset a specific file or directory in Git?
What happens to the commit history when you use git reset?
Can you reset a commit that has already been pushed to the remote repository?
How do you undo a git reset command?
What is the syntax for using git reset?
What are some best practices for using git reset?
How do you use git reset to unstaged changes?
Git Revert:
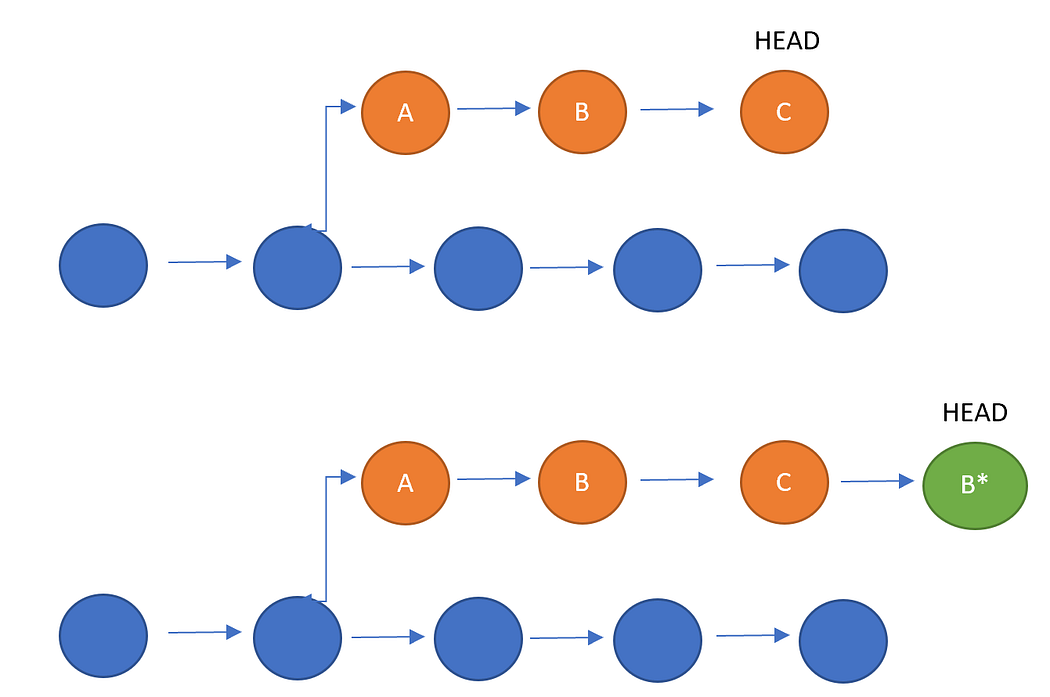
Git revert is a command in Git that is used to undo a previous commit. When you use git revert, a new commit is created that undoes the changes made in the previous commit. This is different from git reset, which removes the previous commit entirely.
The git revert command can be useful if you have made changes to your code that you want to undo, but you don't want to completely remove the commit from your Git history. By using git revert, you can undo the changes while still keeping a record of the original commit.
It's important to note that git reverts only undoes changes made in a single commit. If you want to undo changes made in multiple commits, you'll need to use git revert multiple times.
it doesn't delete any data.
it is reverted to its previous stage and generates a new commit id.
your version control history moves forward while the state of your file moves backwards.
To revert a change that you have committed:
git revert <commit 1> <commit 2>Can you explain the difference between git reset and git revert?

before committing you to use the reset command after committing you to use the revert command
revert is used for public files and reset is used for private files.
How to delete untracked files
git clean -n (dry run)
git clean -f (forcefully)
Tasks For You :
What is git revert and when would you use it?
Can you explain the difference between git reset and git revert?
What happens when you run git revert on a commit that has already been reverted?
How can you revert a merge commit using git revert?
What is the difference between git revert and git cherry-pick?
How can you revert a range of commits using git revert?
What is the advantage of using git revert over git reset for undoing changes?
Can you use git revert to undo changes made to a file in a specific commit?
What happens if a conflict occurs when running git revert?
How can you view the changes made by git revert before committing the changes?
Video Link Here 👇👇👇
TAGS:
A tag in Git is like a bookmark that marks a specific point in a project's history, making it easier to return to that point later. It's often used to mark important milestones or specific versions of the code.
To apply tag
git tag -a <tag_name> -m <message> <commit-id>
To see the list of tags
git tag
To see particular commit content by using tag
git show <tag_name>
To delete a tag
git tag -d <tagname>
Video Link Here 👇👇👇
cherry-pick:(particular pick any commit.)
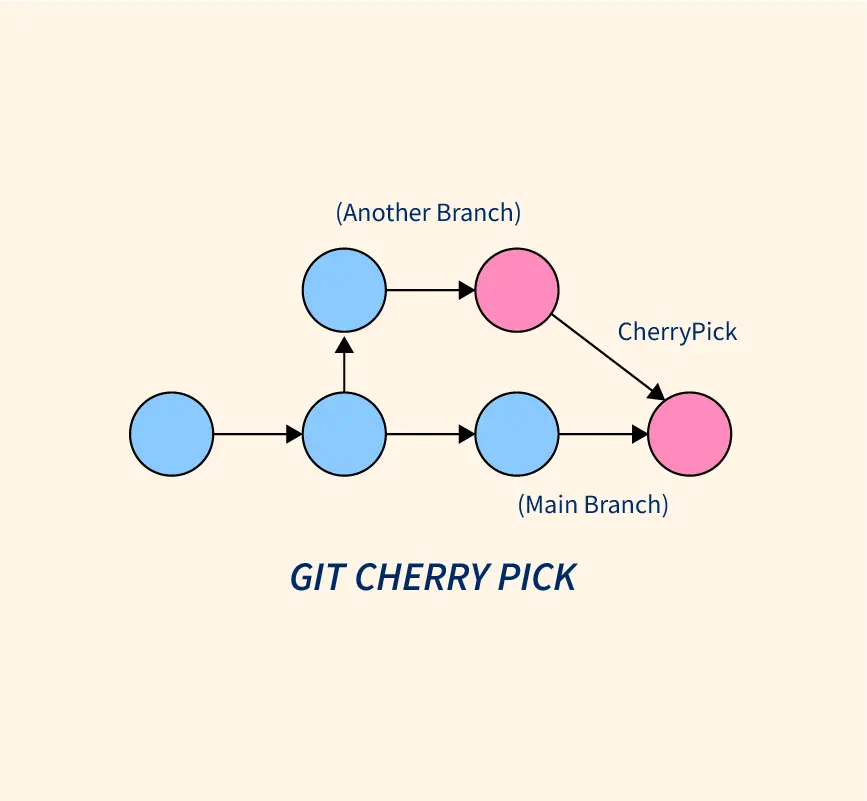
Cherry-picking is a feature in Git that allows you to apply a specific commit from one branch to another. This can be useful if you want to incorporate a particular change or fix into another branch without merging the entire branch. To cherry-pick a commit, you simply identify the commit hash and apply it to the target branch using the git cherry-pick command. This creates a new commit in the target branch with the changes from the original commit. Keep in mind that cherry-picking can lead to conflicts if the same changes have already been made in the target branch, so it's important to review the changes carefully before applying them.
Usage
$ git cherry-pick <commit-hash>
Git cherry-pick doesn’t modify the history of a repository; instead, it adds to the history.


Rebase:

Git rebase is similar to the git merge command. It integrates two branches into a single branch with one exception. A git rebase command rewrites the commit history.
$ git rebase <base>

What is the difference between pull and clone in git?
In Git, "clone" is used to create a copy of a remote repository on your local machine. It downloads the entire repository with all its contents and version history.
On the other hand, "pull" is used to update your local repository with the changes made in the remote repository. It only downloads the changes made since your last update and merges them with your local repository.
So, in simple terms, "clone" is used to download the entire repository for the first time, while "pull" is used to download only the changes made since your last update.
Difference between merging and rebasing
Merging and rebasing are two different ways to integrate changes from one branch into another. Merging creates a new commit that combines the changes from the source branch into the destination branch. This results in a merge commit that has two parent commits, one from each branch. Merging is useful when you want to preserve the entire history of the source branch, and when there are multiple contributors making changes to the same codebase.
On the other hand, rebasing moves the entire source branch to the tip of the destination branch, effectively re-writing the history of the source branch. This creates a linear history as if all the changes were made on a single branch. Rebasing is useful when you want to keep the commit history clean and easy to understand, and when you want to avoid merge conflicts by incorporating changes from the destination branch before applying your changes.

In summary, merging creates a new commit that combines changes from two branches, while rebasing moves the entire source branch to the tip of the destination branch, resulting in a linear history of changes.

