What are Services in K8s
In Kubernetes, Services are objects that provide stable network identities to Pods and abstract away the details of Pod IP addresses. Services allow Pods to receive traffic from other Pods, Services, and external clients.
What are the different services within Kubernetes?
Different types of Kubernetes services include:
Cluster IP service
Node Port service
External Name Creation service and
Load Balancer service
What is ClusterIP?
The ClusterIP is the default Kubernetes service that provides a service inside a cluster (with no external access) that other apps inside your cluster can access.
What is NodePort?
The NodePort service is the most fundamental way to get external traffic directly to your service. It opens a specific port on all Nodes and forwards any traffic sent to this port to the service
What is the LoadBalancer in Kubernetes?
The LoadBalancer service is used to expose services to the internet. A Network load balancer, for example, creates a single IP address that forwards all traffic to your service.
In Kubernetes, what is the difference between a service and a deployment?
In Kubernetes a deployment is a method of launching a pod with containerized applications and ensuring that the necessary number of replicas is always running on the cluster.
On the other hand, a service is responsible for exposing an interface to those pods, which enables network access from either within the cluster or between external processes and the service.
Pre-Requisites:- You should have the following installed in your instance:
Docker
Minikube
Kubectl
Task-1:
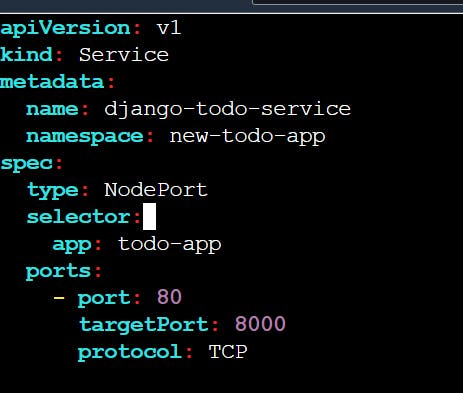
Create a Service for your todo-app Deployment from Day-32
Create a Service definition for your todo-app Deployment in a YAML file.
Apply the Service definition to your K8s (minikube) cluster using the
kubectl apply -f service.yml -n <namespace-name>command.Verify that the Service is working by accessing the todo-app using the Service's IP and Port in your Namespace.
SOLUTION:
kubectl create namespace new-todo-appkubectl get namespaces
vim deployment.yaml
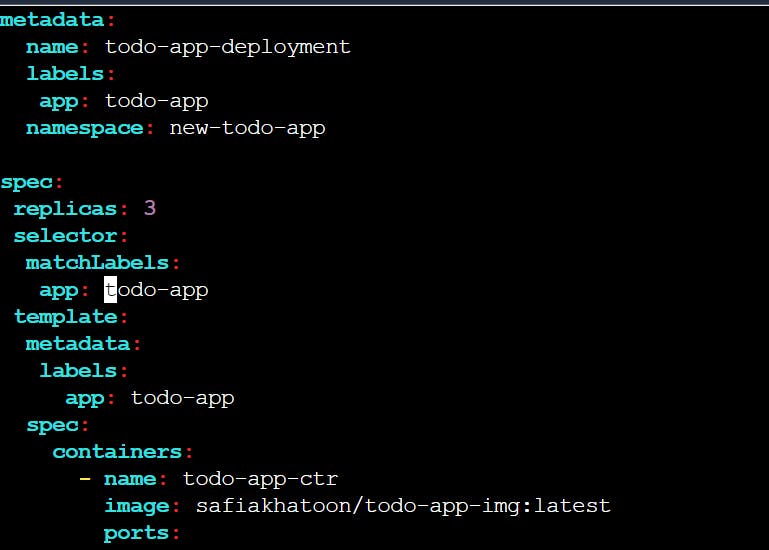
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml
kubectl get pods -n new-todo-app -o wide
vim service.yaml
kubectl apply -f service.yaml

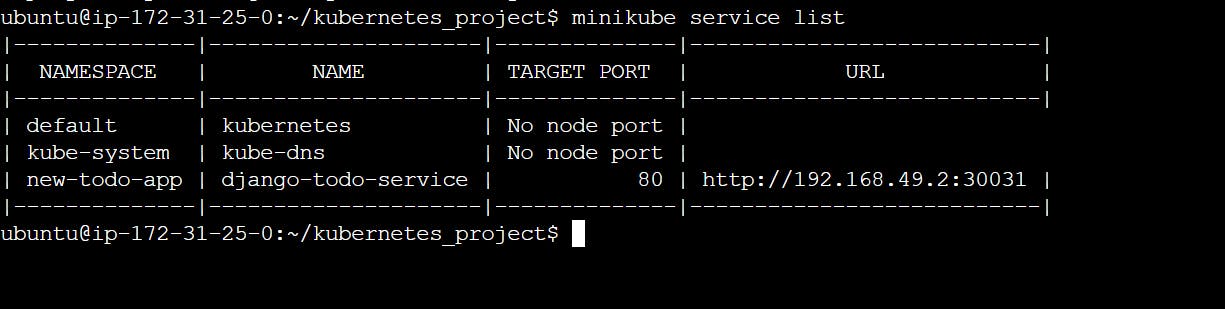
minikube service list
curl -L http://192.168.49.2:30031
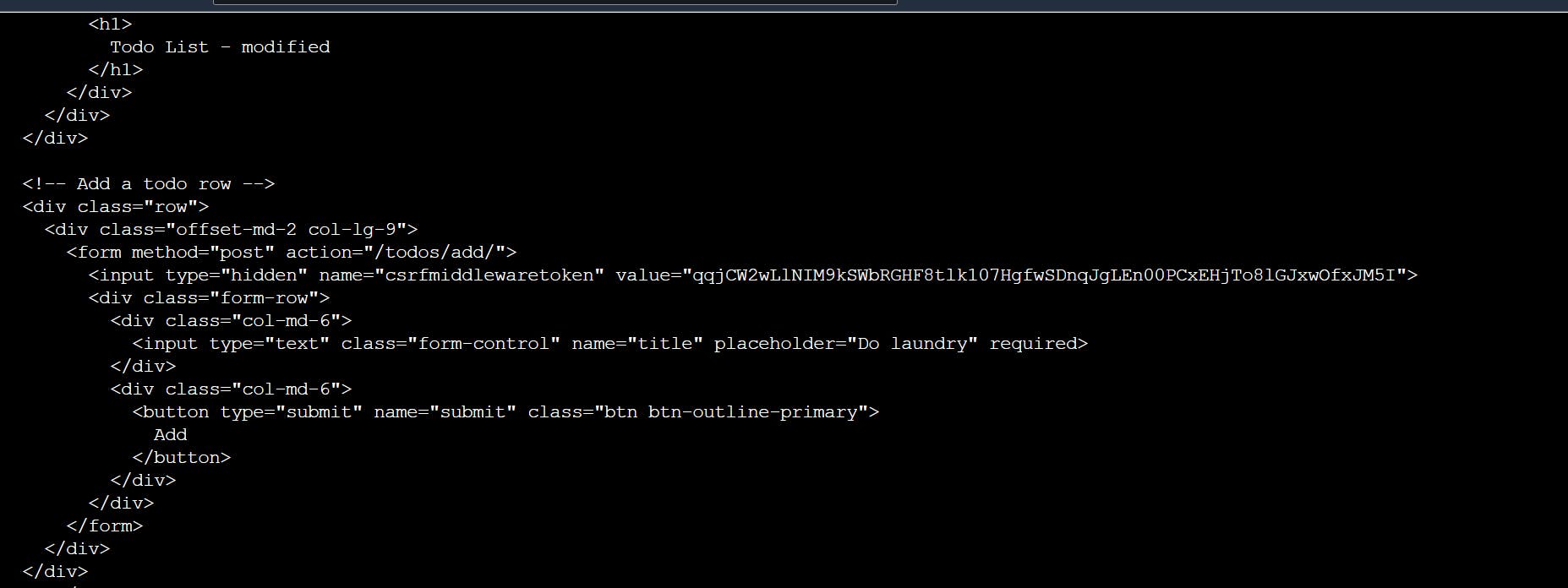

Now we need to make our IP public. For this, we’ll be making use of ngrok.
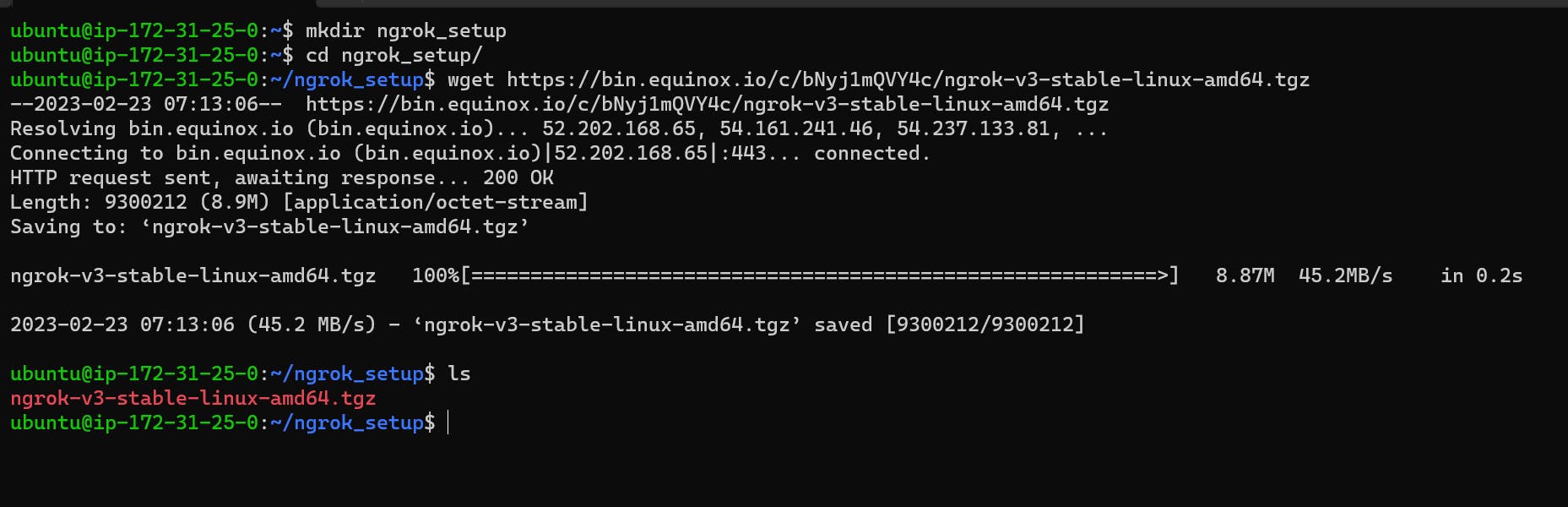
wget https://bin.equinox.io/c/bNyj1mQVY4c/ngrok-v3-stable-linux-amd64.tgz
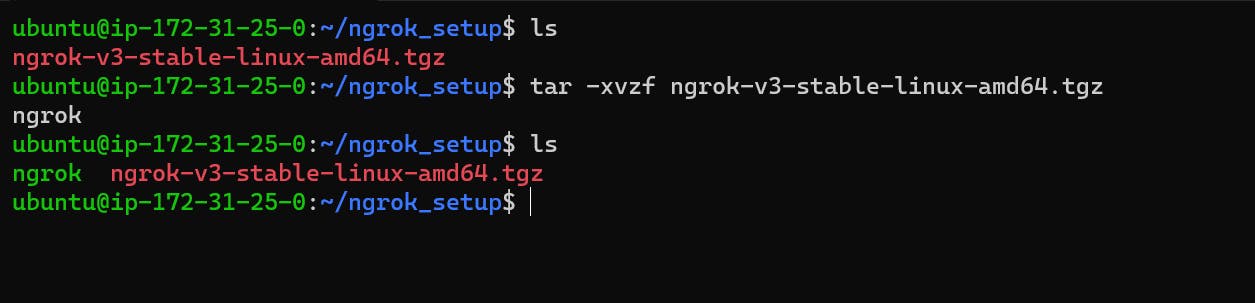
tar -xvzf ngrok-v3-stable-linux-amd64.tgz
ngrok config add-authtoken 2M5QFMKfa2G4MXUHUDEqGnrJhlk_5LJBPXZSJhYki63CpfNHv

sudo snap install ngrok
./ngrok config add-authtoken 2M5QFMKfa2G4MXUHUDEqGnrJhlk_5LJBPXZSJhYki63CpfNHv

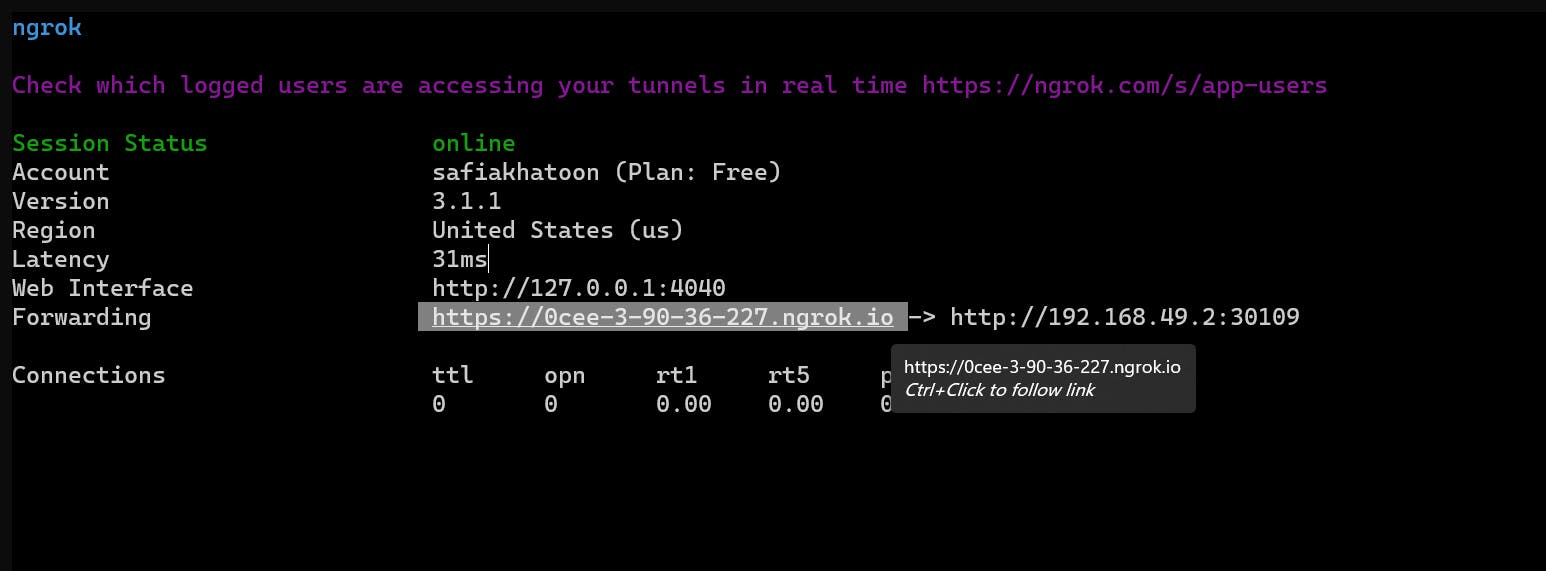
./ngrok http 192.168.49.2:30109
Task-2:
Create a ClusterIP Service for accessing the todo-app from within the cluster
Create a ClusterIP Service definition for your todo-app Deployment in a YAML file.
Apply the ClusterIP Service definition to your K8s (minikube) cluster using the
kubectl apply -f cluster-ip-service.yml -n <namespace-name>command.Verify that the ClusterIP Service is working by accessing the todo-app from another Pod in the cluster in your Namespace.
solution:
vim deployment.yaml

kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml
kubectl get pods -n todo-app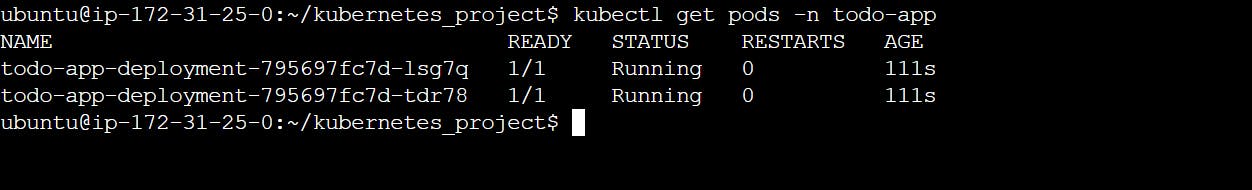
Now make a new service file using command “vim service.yaml”
vim service.yaml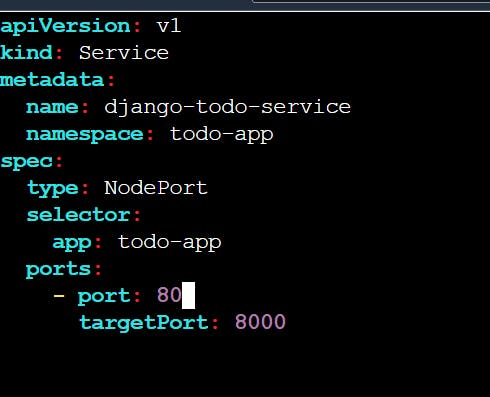
kubectl apply -f service.yaml
kubectl get pods -n todo-app
minikube service list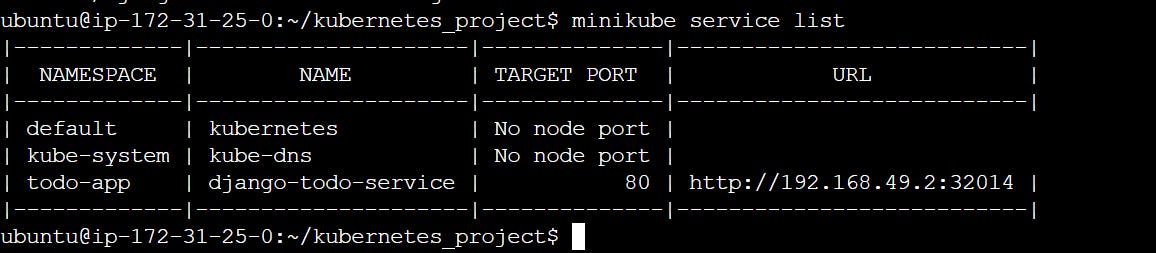
curl -L http://192.168.49.2:32014
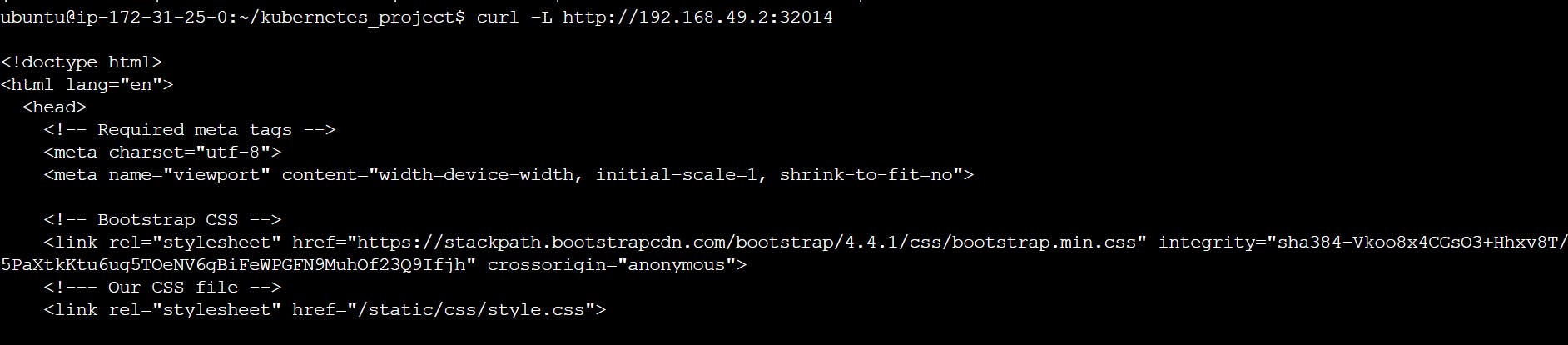
Now we need to make our IP public. For this, we’ll be making use of ngrok.
wget https://bin.equinox.io/c/bNyj1mQVY4c/ngrok-v3-stable-linux-amd64.tgz

wget https://bin.equinox.io/c/bNyj1mQVY4c/ngrok-v3-stable-linux-amd64.tgz
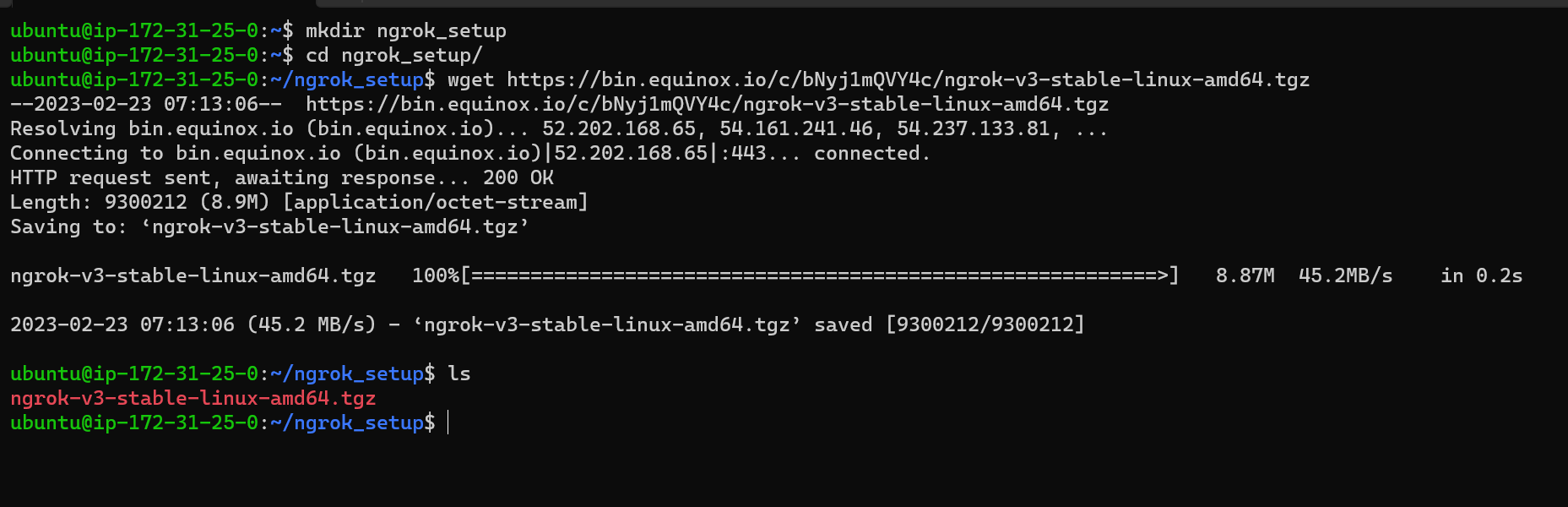
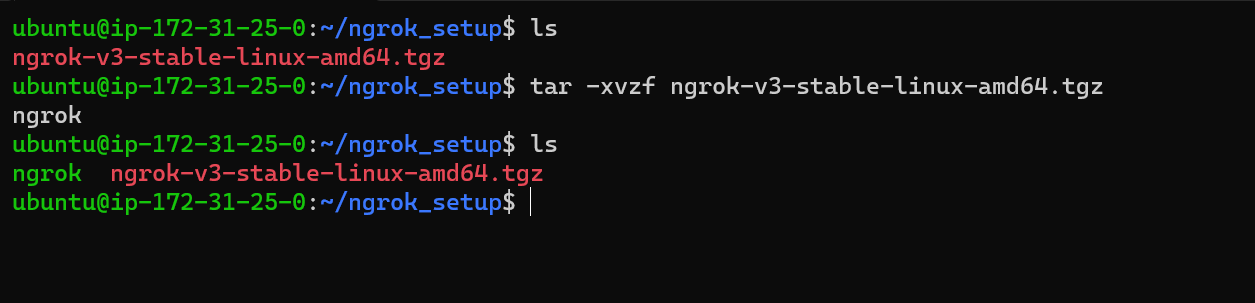
tar -xvzf ngrok-v3-stable-linux-amd64.tgz
ngrok config add-authtoken 2M5QFMKfa2G4MXUHUDEqGnrJhlk_5LJBPXZSJhYki63CpfNHv

sudo snap install ngrok
./ngrok config add-authtoken 2M5QFMKfa2G4MXUHUDEqGnrJhlk_5LJBPXZSJhYki63CpfNHv

./ngrok http 192.168.49.2:30109

Task-3:
Create a LoadBalancer Service for accessing the todo-app from outside the cluster
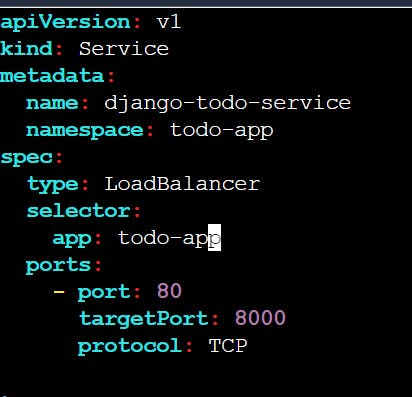
Create a LoadBalancer Service definition for your todo-app Deployment in a YAML file.
Apply the LoadBalancer Service definition to your K8s (minikube) cluster using the
kubectl apply -f load-balancer-service.yml -n <namespace-name>command.Verify that the LoadBalancer Service is working by accessing the todo-app from outside the cluster in your Namespace.

kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml
kubectl get pods --namespace=todo-app

vim service.yaml
kubectl apply -f service.yaml
kubectl get svc -n todo-app
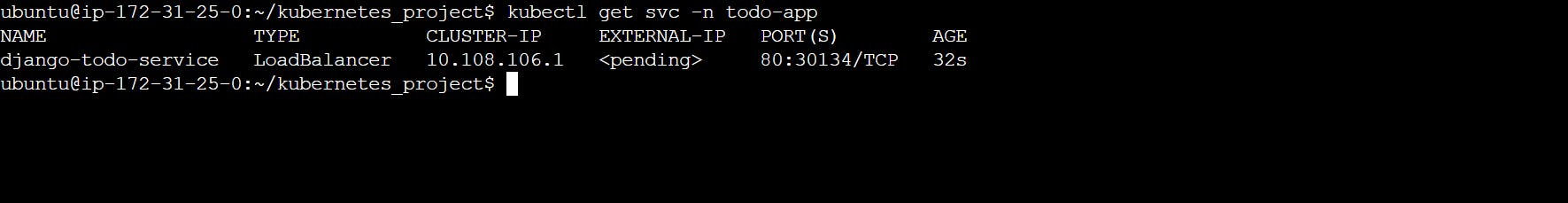
where,
svc - service
-n = namespace
this ip is k8s cluster ip not my ubuntu ip
minikube service django-todo-service -n todo-app --url
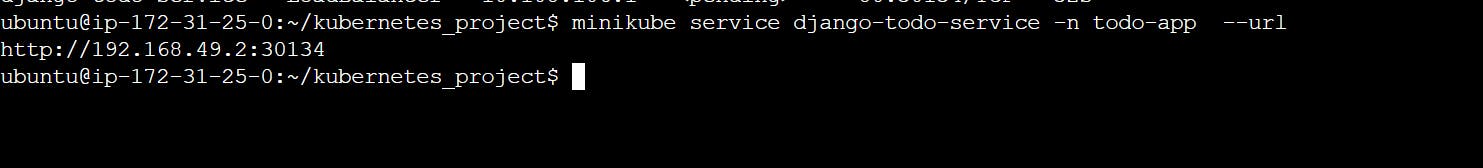
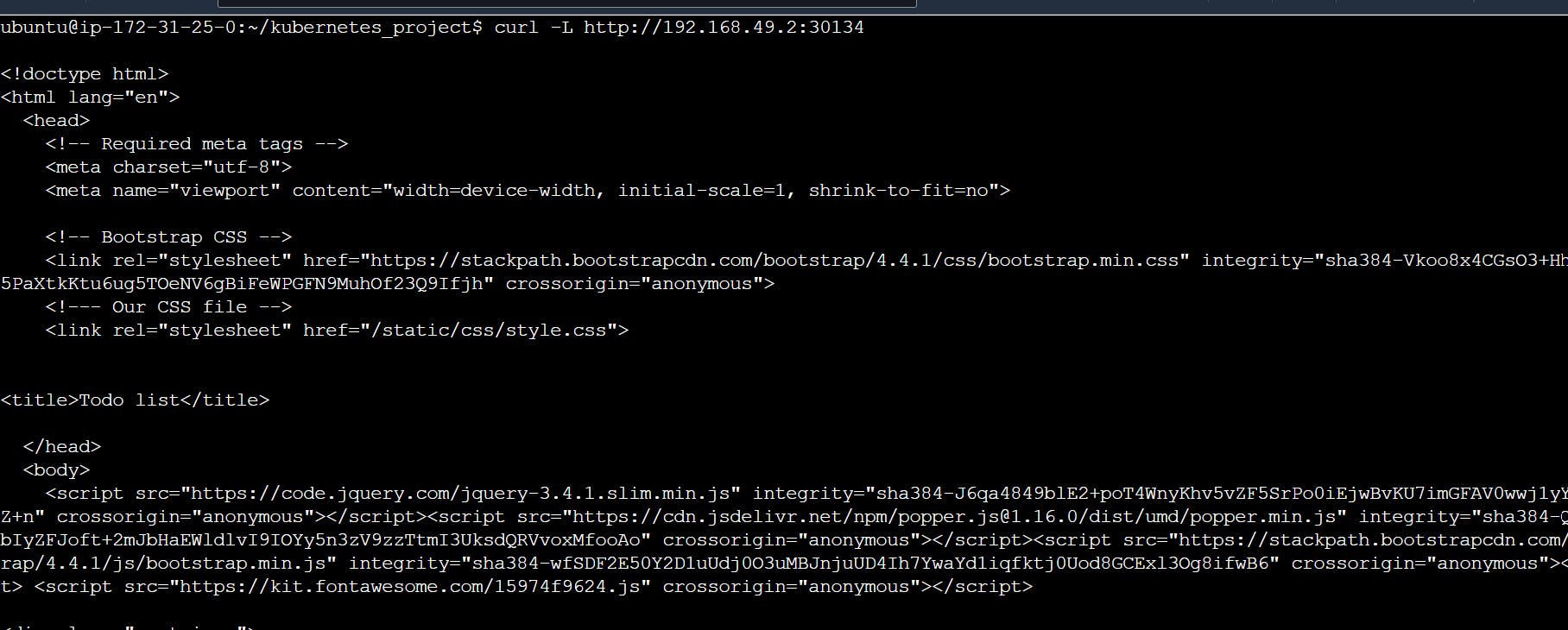
curl -L http://192.168.49.2:30134


If you want to access your app on the browser so there is a concept called NGROK

click on sign up for free

wget https://bin.equinox.io/c/bNyj1mQVY4c/ngrok-v3-stable-linux-amd64.tgz

tar -xvzf ngrok-v3-stable-linux-amd64.tgz

x - for extract
v- for verbose
z- for gunzip
f- for file, should come at last just before the file name.
ngrok config add-authtoken 2M5QFMKfa2G4MXUHUDEqGnrJhlk_5LJBPXZSJhYki63CpfNHv

sudo snap install ngrok

./ngrok config add-authtoken 2M5QFMKfa2G4MXUHUDEqGnrJhlk_5LJBPXZSJhYki63CpfNHv

./ngrok http 192.168.49.2:30109


Thanks for reading the blog. Hope it helps.
— Safia Khatoon
Happy Learning :)